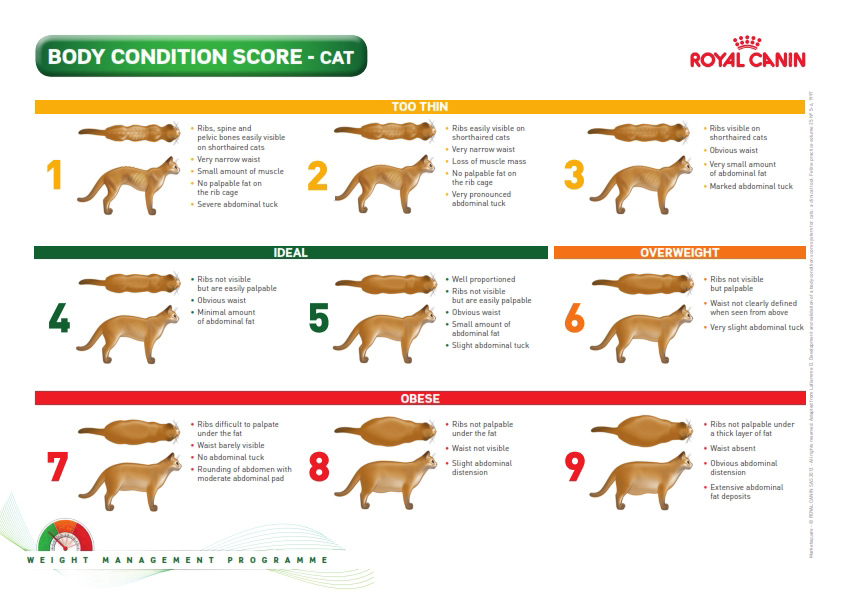
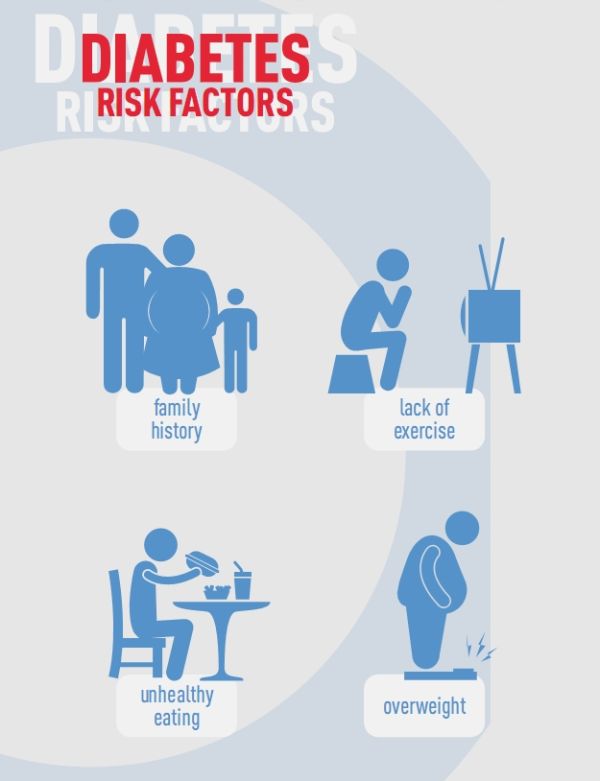
Diet, nutrition and the prevention of excess weight gain and obesity BA Swinburn1, , I Caterson2, JC Seidell3 and WPT James4 1Physical Activity and Nutrition Research Unit, School of Health Sciences, Deakin University, Melbourne, Australia: 2Faculty of Medicine, University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia: 3Free University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 4International Obesity Task Force. Your food choices each day affect your health how you feel today, tomorrow, and in the future. Good nutrition is an important part of leading a healthy lifestyle. At the other end of the malnutrition scale, obesity is one of todays most blatantly visible yet most neglected public health problems. Paradoxically coexisting with undernutrition, an escalating global epidemic of overweight and obesity globesity is taking over many parts of. About feline diabetes and its relationship to diet. Elizabeth Hodgkins articulates the need to adhere to commonsense principles in feeding cats as carnivores in this insightful article, which she has very kindly given me permission to publish on this site. Held Annually, the World Congress on Nutrition and Obesity Prevention Source will be one of the worldleading conferences in the Nutrition and Obesity. Context As a result of changes in the way we eat and live, some chronic diseases are increasingly affecting both developed and developing countries. Indeed, dietrelated chronic diseases such as obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, cancer, dental disease, and osteoporosis are the most common cause of death in the world and present a great burden for society. Being overweight or obese increases the chances of developing the common type of diabetes, type 2 diabetes. Nutrition is the science that interprets the interaction of nutrients and other substances in food in relation to maintenance, growth, reproduction, health and disease of an organism. It includes food intake, absorption, assimilation, biosynthesis, catabolism, and excretion. The diet of an organism is what it eats, which is largely determined by the availability and palatability of foods. Allison is the current dean, distinguished professor, and provost professor at the Indiana University School of Public HealthBloomington. Prior to Indiana University, Allison was a distinguished professor, Quetelet Endowed Professor, and director of the NIHfunded Nutrition Obesity Research Center (NORC) at the University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB). CDC's Obesity efforts focus on policy and environmental strategies to make healthy eating and active living accessible and affordable for everyone. Medical nutrition therapy (MNT) is important in preventing diabetes, managing existing diabetes, and preventing, or at least slowing, the rate of development of diabetes complications. It is, therefore, important at all levels of diabetes prevention (see Table 1). MNT is also an integral component of diabetes selfmanagement education (or training). CDCs Division of Nutrition, Physical Activity and Obesity (DNPAO) protects the health of Americans at every stage of life by encouraging regular physical activity, good nutrition, and preventing adult and childhood obesity. MS in Nutrition Sciences, Dietitian Education Program. With at least a bachelors degree from any area of study with science and nutrition course prerequisites, the MS in Nutrition Sciences, Dietitian Education Program has two options: the Dietitian Education Program Track (DEP) and the Dietitian Education Program Graduate Certificate (DEPC). Welcome to the Section of Endocrinology, Diabetes, Nutrition and Weight Management Clinical Activities. The Endocrinology, Diabetes, Nutrition and Weight Management Clinic is located in the newly renovated space on Preston 2. Obesity is a medical condition in which excess body fat has accumulated to the extent that it may have a negative effect on health. People are generally considered obese when their body mass index (BMI), a measurement obtained by dividing a person's weight by the square of the person's height, is over 30 kgm 2, with the range 2530 kgm 2 defined as overweight. Stop Eating Yourself Sick Take Control Of Your Health The United States will not be able to afford metabolic syndrome, a combination of disorders including obesity, diabetes. Experts now predict that more than onethird of American children born in 2000 will develop diabetes in their lifetime. Written by one of the world's leading authorities on the link between obesity and diabetes, this passionate, frighteningbut ultimately hopefulbook points the way to a solution. gov is a USDAsponsored website that offers credible information to help you make healthful eating choices. BELIEFS ABOUT NUTRITION ARE BASED ON VERY LITTLE SCIENTIFIC EVIDENCE. The mission of Nutrition Science Initiative is to reduce the individual, social, and economic costs of obesity, diabetes, and their related diseases by improving the quality of science in nutrition and obesity. Food and beverages provide the energy and nutrients you need to improve health, manage disease, and reduce the risk of disease. Find resources on nutrition to help you pay attention to what, when, how often, why, and how much you eat and drink, as well as, help manage health conditions such as diabetes, obesity, kidney disease, and others. An international, peer reviewed, open access, online journal. The journal is committed to the rapid publication of the latest laboratory and clinical findings in the fields of diabetes, metabolic syndrome and obesity research. If type 2 diabetes was an infectious disease, passed from one person to another, public health officials would say were in the midst of an epidemic. This difficult disease, once called adultonset diabetes, is striking an evergrowing number of adults. Even more alarming, its now beginning to. Most patients with type 2 diabetes are obese, and the global epidemic of obesity largely explains the dramatic increase in the incidence and prevalence of type 2 diabetes over the past 20 years. In recent years, the face of type 2 diabetes has changed rapidly, with the disease affecting growing numbers of adolescents and children. Obesity is strongly associated with type 2 diabetes, and it is predicted that onethird of all children born today will develop type 2 diabetes in their lifetime. 1 The serious longterm health consequences of type 2 diabetes, including elevated risk of. Diabetes is a disease that occurs when your blood glucose, also called blood sugar, is too high. Over time, having too much glucose in your blood can cause health problems, such as heart disease, nerve damage, eye problems, and kidney disease..